Technological Leap: Innovations Through the Ages
28 October, 2024
Industrial revolutions have marked pivotal shifts in history, reshaping economies and societies through groundbreaking technological progress.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is more than just another phase that's transforming industries. By 2025, it is projected to generate an impressive $3.7 trillion in value, driven by advancements in AI, automation, and data analytics, which promise to boost productivity, enhance quality of life, and fuel sustainable growth on a global scale (MIT Technology Review Insights).
As enterprises leverage the Internet of Things (IoT), Industry 5.0 emerges, shifting from automation to a human-centric approach where collaboration between people and machines drives creativity and faster problem-solving.
We’ll explore these breakthroughs and their lasting impact on industries, particularly regarding personalization, sustainability, and the future of work.

The Five Industrial Revolutions: Cornerstones of Modern Manufacturing
Manufacturing has been reshaped through five distinct industrial revolutions, each defined by technological breakthroughs that transform production. From the rise of mechanization to today's human-centric approaches, these revolutions continuously shape how industries operate and innovate.
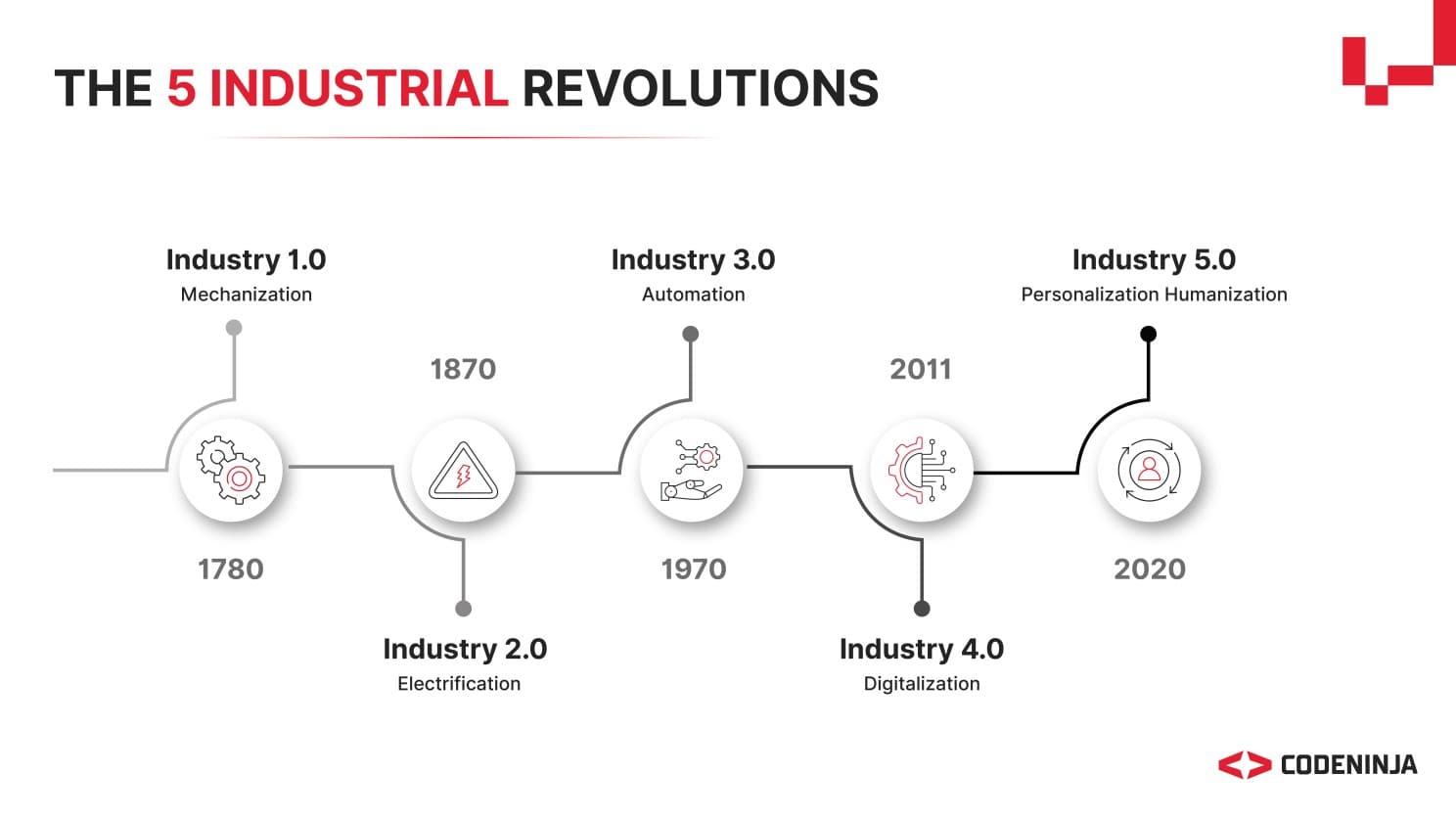
Industrial Revolution 1.0 - Mechanization (1780)
The First Industrial Revolution, which began in late 18th-century Britain, introduced the steam engine and mechanized machinery, drastically reducing reliance on human and animal labor. This shift enabled mass production in factories, transforming manufacturing processes.
As goods became machine-made instead of handcrafted, urbanization surged, changing labor dynamics and reshaping society. This revolution laid the foundation for modern industry and paved the way for future advancements.
Industrial Revolution 2.0 - Electrification (1870)
The Second Industrial Revolution began around 1870, introducing mass production and assembly lines powered by electricity, oil, and gas. These innovations streamlined manufacturing, increasing efficiency and enabling the widespread availability of consumer goods.
The rise of assembly lines also marked the beginning of labor rights movements, as workers sought improved conditions in the increasingly mechanized industries. This era established modern manufacturing practices that continue to influence production today.
Industrial Revolution 3.0 - Automation (1970)
The Third Industrial Revolution began in the mid-20th century, introducing computers and robotics to manufacturing. This era saw factories digitize with programmable logic controllers (PLCs), which automated processes and improved data collection. Enhanced efficiency and precision transformed operations, while labor roles evolved, focusing more on data management and analysis. This revolution laid the groundwork for the smart manufacturing techniques we utilize today.
Industrial Revolution 4.0 - Digitalization (2011)
Industry 4.0 transformed manufacturing through technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), AI, and machine learning. These innovations enabled the creation of smart factories where connected devices collected real-time data, enhancing decision-making and efficiency. Cloud and edge computing facilitated quick data processing and responsiveness. Industry 4.0 solutions have propelled industries to harness the next wave of innovation for smarter decision-making.

Industrial Revolution 5.0 - Personalization and Humanization (2020)
The fifth industrial revolution emphasizes a human-centric approach, where technology enhances human creativity and fosters effective collaboration between people and machines.
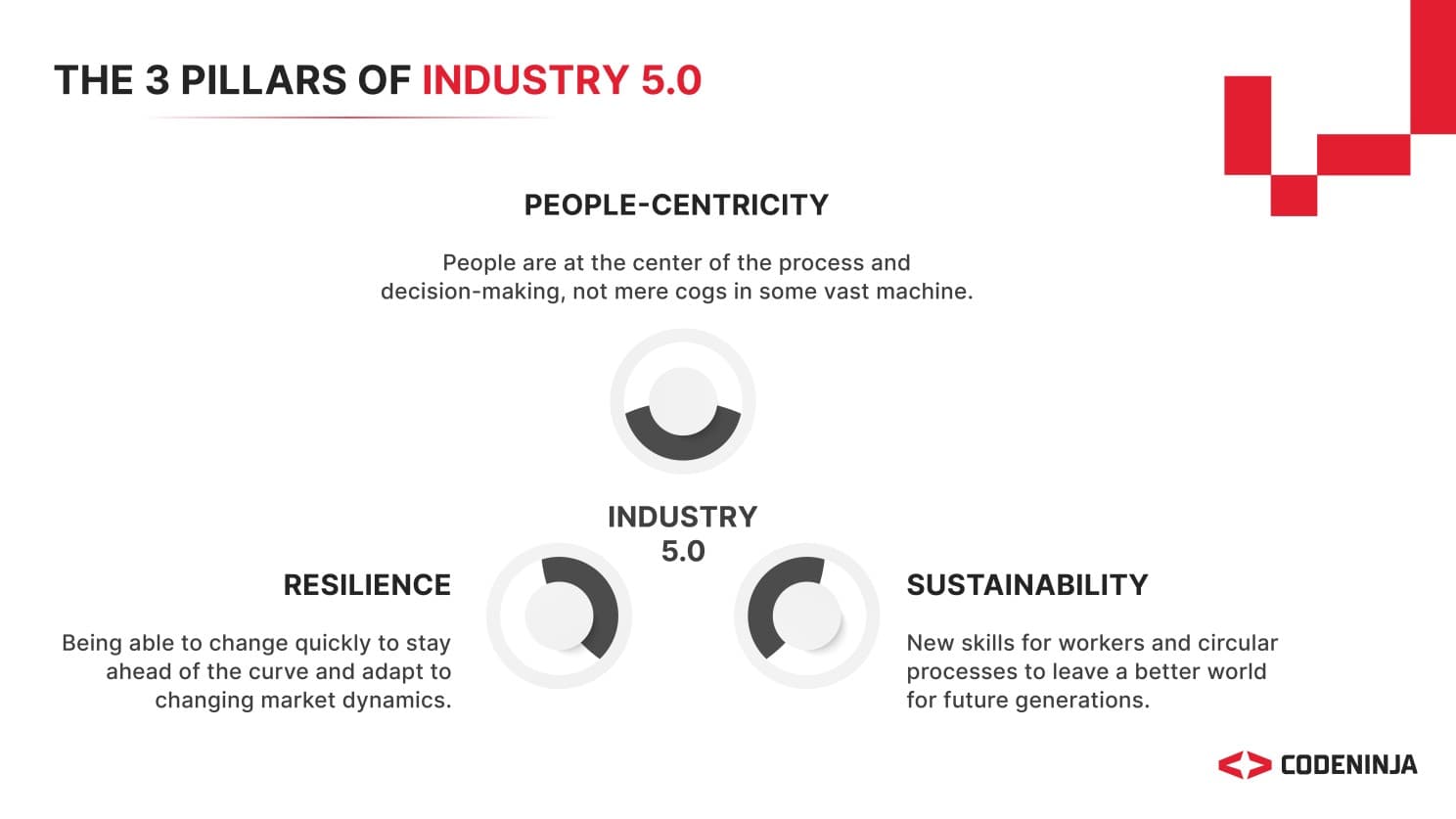
This era is defined by three pillars: human-centricity, which places people at the heart of processes; resilience, enabling rapid adaptation to change; and sustainability, promoting ethical practices and resource efficiency.
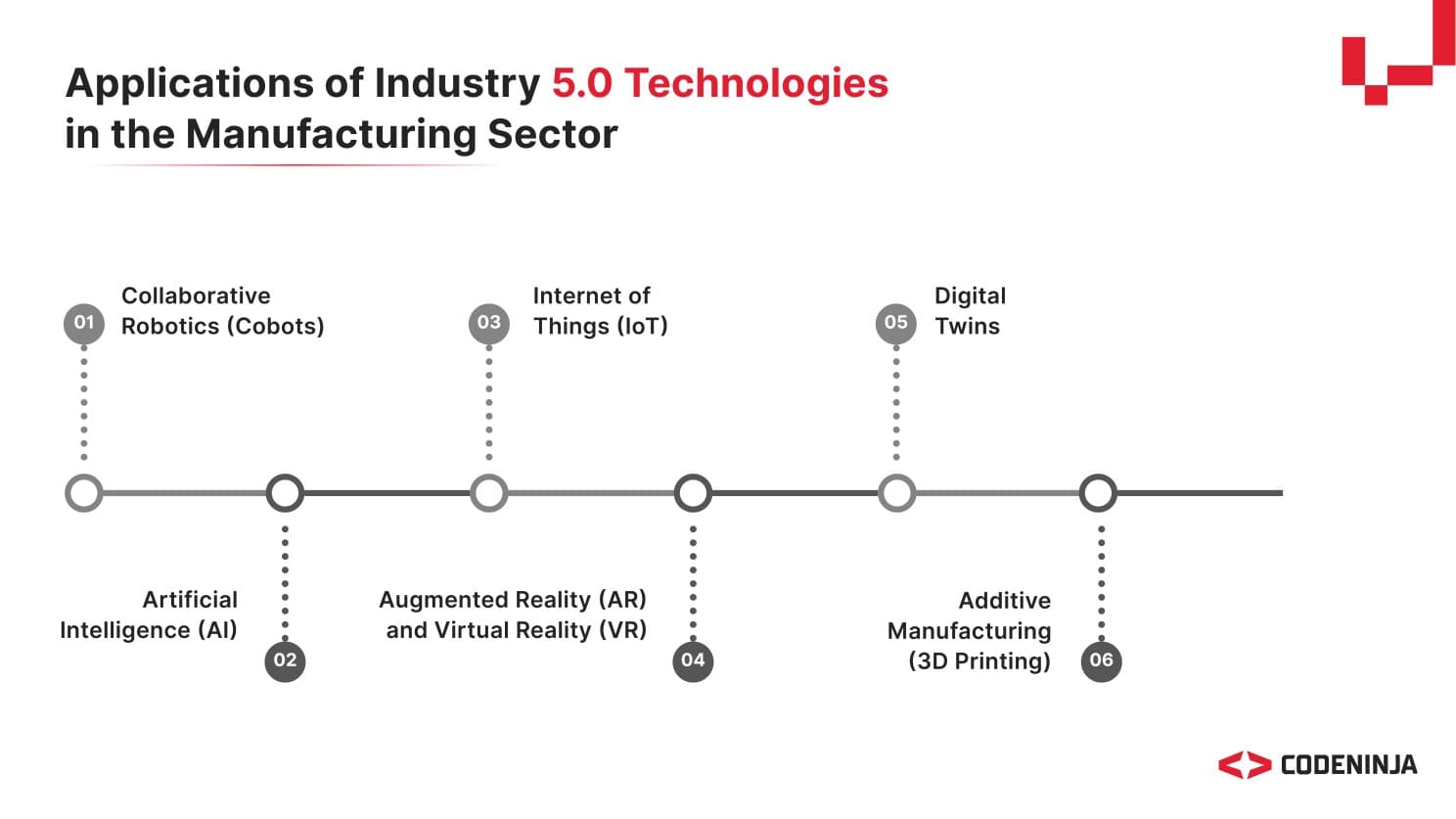
Collaborative robots work alongside humans to enhance production processes while promoting personalized manufacturing. By harnessing advanced AI, IoT, and big data analytics, enterprises can generate insights for quick, informed decision-making and tailor their offerings, minimizing waste. This synergy not only boosts productivity but also ensures human values remain central in industrial practices.
Industry 5.0 redefines manufacturing, enhancing workforce engagement and making people integral to the production landscape, paving the way for a more sustainable and personalized future in manufacturing.
Analytical Insights on Industrial Revolutions
The four big shifts in manufacturing over the last 275 years highlight key changes from mechanization to digitization. Each industrial revolution has reshaped worker roles, machine autonomy, and production processes.
This section explores how these technological advancements transformed not just manufacturing, but also labor markets and consumer behavior, leading to a more personalized and sustainable industry landscape.
The insights gained from these shifts provide a foundation for understanding the future of manufacturing in the context of Industry 4.0 and beyond.
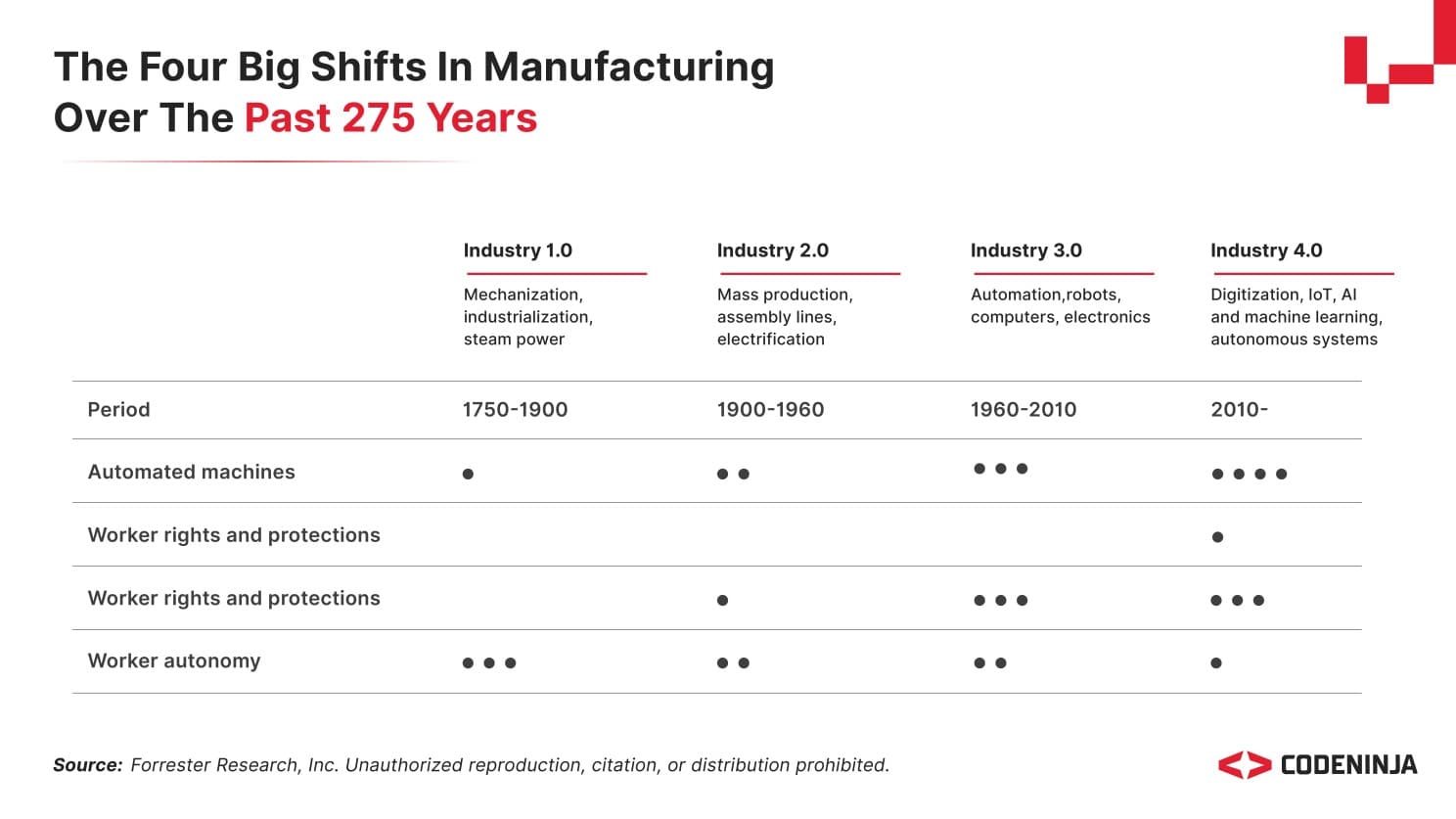
Technological Acceleration and Social Impact
The industrial revolutions have driven significant technological advancements, from the steam engine in Industry 1.0 to AI and IoT in Industry 4.0, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Each revolution has also reshaped labor markets and urbanization, altering consumer behavior and work dynamics. Mechanization drew workers to cities, while automation and digitalization transformed job roles, increasing the demand for new skills.
Enterprises that invest in continuous employee development and foster collaboration with technology will thrive in this evolving landscape, ultimately navigating the industrial shifts successfully.
The Evolution of Production Models
The transition from mass production to personalized production represents a significant shift in manufacturing, driven by Industry 4.0 technologies. Innovations like IoT, AI, and data analytics allow manufacturers to efficiently customize products to meet individual consumer preferences, enhancing satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Data plays a vital role in this evolution, enabling enterprises to refine strategies, predict trends, and optimize operations, ensuring that personalization aligns with market demands.
Sustainability and Ethical Production
In Industry 5.0, sustainability and ethical production are key focuses, blending human creativity with machine precision to minimize waste and enhance energy efficiency.
Advanced technologies, like AI-driven optimization, allow businesses to use resources wisely and tackle environmental challenges. This collaboration ensures that technological growth respects both people and the planet, emphasizing the importance of balancing innovation with social responsibility for a more sustainable manufacturing landscape.
Challenges and Opportunities in Adoption
Businesses face high implementation costs, technical complexities, and integration hurdles. Workforce transition requires investment in education for AI, robotics, and data analysis. Additionally, as data collection increases, compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA becomes essential to protect consumer rights.
Despite these challenges, new frontier technologies present enterprises with the chance to deliver personalized products, enhance competitiveness, and drive long-term economic growth while ensuring responsible data practices.
Future of Work in a Technological Landscape
Industry 5.0 will significantly transform workforce dynamics as automation and AI reshape roles, emphasizing the need for continuous reskilling. The integration of hybrid intelligence—where humans and machines collaborate—will drive innovation and enhance productivity.
Looking ahead, we can expect AI-driven manufacturing, personalized production, and sustainability to shape Industry 5.0. Technological breakthroughs in robotics and quantum computing will further enhance efficiency, revolutionizing manufacturing and global supply chains, and creating new opportunities while requiring adaptive changes in supply chain management.
As we navigate the ongoing industrial revolutions, each phase—from mechanization to Industry 5.0—has introduced innovations that enhance efficiency, personalization, and sustainability. By blending human creativity with machine precision, the future of manufacturing is not only about technological advancement but also about reshaping industries for a more ethical, inclusive, and sustainable world.
At CodeNinja, we are committed to harnessing AI and transformative technology that is rooted in the principles of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 in collaboration with frontier technology partners to empower enterprises across industries.
Visit our website to learn more about how our solutions can support your journey in this evolving landscape.
