Harnessing AI/ML & Simulation for a Smarter Industry 4.0 Transformation
29 November, 2024
As businesses strive to stay competitive in the Industry 4.0 era, the need for smarter, more efficient operations has never been greater. Machine learning (ML) and simulation technologies are at the forefront of this transformation, enabling businesses to predict, optimize, and innovate like never before.
With over 70% of manufacturers expected to integrate ML-driven predictive analytics by 2030 (McKinsey), the impact of these technologies is undeniable.
From predictive maintenance to real-time training and risk-free testing, these technologies not only drive operational efficiency but also help businesses overcome common challenges like cost overruns, resource inefficiencies, and slow adaptability, shaping the future of manufacturing.
Decoding ML and Simulation Technologies
In the era of Industry 4.0, machine learning (ML) and simulation technologies are transforming manufacturing operations. ML algorithms analyze vast datasets from production lines, equipment, and products to predict outcomes, optimize maintenance schedules, enhance quality control, and improve product design. These predictive insights drive efficiencies and reduce costs across the production cycle.
Simulations, powered by AR, VR, and MR, create virtual replicas of manufacturing systems, enabling risk-free testing, workflow optimization, and assembly line validation. For instance, VR can train workers in equipment operation, while AR offers real-time assembly guidance. Simulation tools also model potential disruptions in the supply chain, empowering businesses to develop more resilient and effective strategies. Together, ML and simulations help manufacturers streamline processes, enhance productivity, and foster innovation.
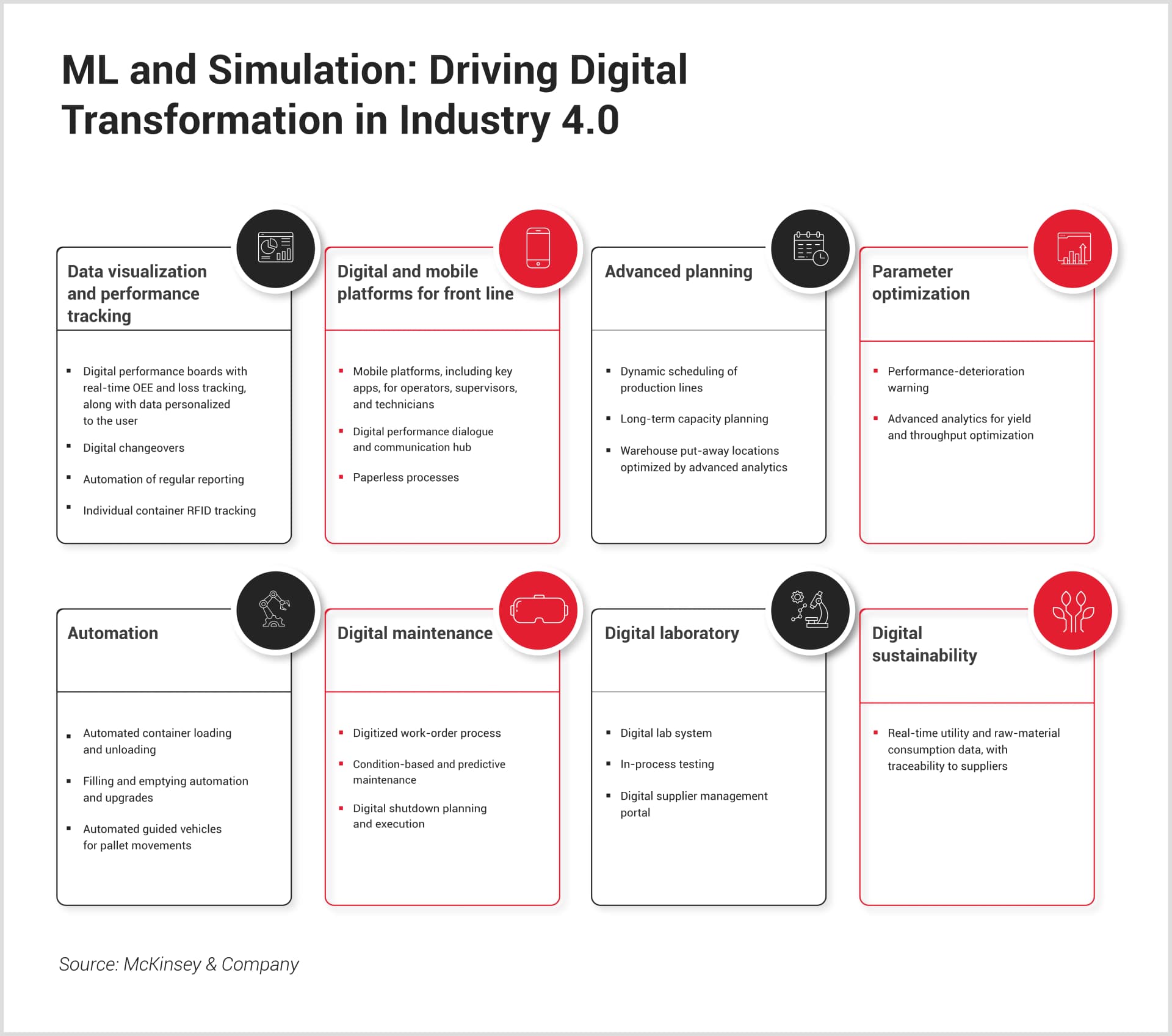
How ML and Simulation Synergize to Accelerate Digital Transformation
The integration of ML and simulation technologies is central to the Industry 4.0 revolution, combining predictive insights with practical validation to drive innovation. ML forecasts issues like equipment failures, while AR/VR/MR simulations optimize workflows and test strategies in real-time, minimizing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
This synergy aligns with the broader digital transformation, reshaping manufacturing by enabling predictive maintenance, streamlining operations, and supporting sustainable practices. Real-time data visualization, automation, and dynamic planning further enhance flexibility and reduce waste, unlocking the full potential of Industry 4.0 to create more efficient and innovative manufacturing environments.
Use Cases of ML and Simulation in Modern Industry
ML and simulation technologies are revolutionizing industrial sectors, driving efficiency, adaptability, and innovation, and fueling digital transformation with groundbreaking advancements.
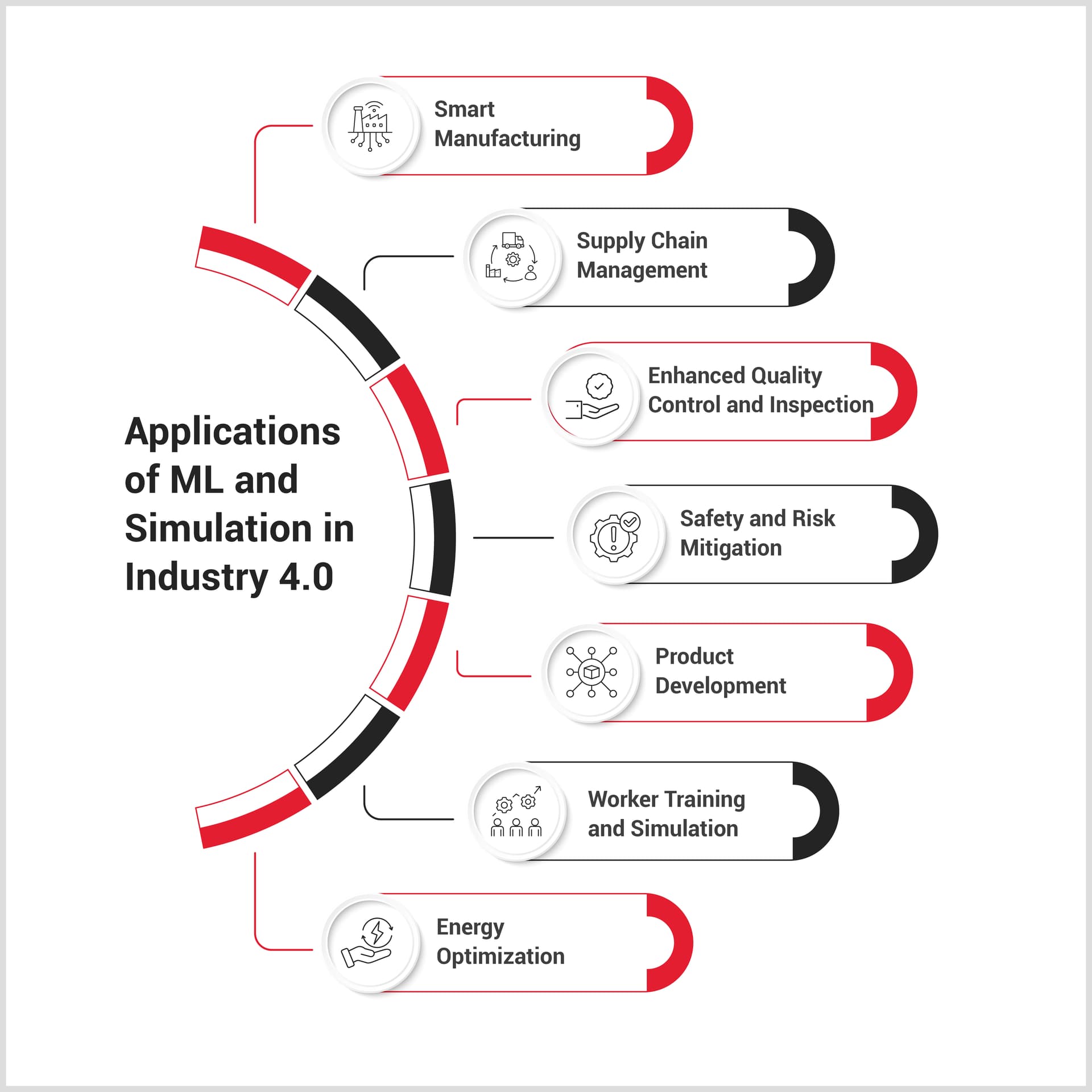
Smart Manufacturing
Smart Manufacturing
ML predicts equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance that reduces downtime and costs. Simulations, like digital twins, optimize factory layouts and workflows before implementation, minimizing disruptions and saving resources.
Supply Chain Management
Machine Learning can reduce supply chain forecasting errors by 50% and lost sales by 65% through improved product availability (McKinsey). Simulations complement this by modeling disruptions like port delays, enabling businesses to build more resilient and agile supply chains.
Enhanced Quality Control and Inspection
AR systems assist in real-time quality control by overlaying product specifications and tolerances on physical items, allowing workers to verify dimensions and detect defects more effectively during production.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
VR simulations are used to train workers in high-risk environments, preparing them for emergencies or hazardous tasks without exposing them to actual dangers. This enhances workplace safety by familiarizing employees with potential risks and safety procedures.
Product Development
ML drives product customization by analyzing consumer data, while simulations test virtual prototypes, reducing physical trials. This accelerates time-to-market, cuts costs, and fosters innovation through rapid design iterations.
Worker Training and Simulation
VR and MR simulations create immersive, risk-free environments for training workers on complex machinery and factory processes. This approach ensures high-quality, hands-on learning experiences without the risks of live production environments.
Energy Optimization
ML identifies inefficiencies in energy use, while simulations predict the impact of optimization strategies. Together, they enable energy-saving measures, reduce waste, and support sustainability goals, lowering operational expenses.
The Impact of ML and Simulation Technologies
The integration of ML and simulation have revolutionized industrial operations, driving efficiency, productivity, and cost savings.
By optimizing inventory management, boosting labor productivity, reducing downtime, and improving forecasting accuracy, these technologies have reshaped workflows, enhanced quality, and delivered significant operational improvements.

Challenges and Limitations of ML and Simulation in Modern Industries
Adopting ML and simulation technologies presents multiple challenges, including data quality, legacy system integration, resource allocation, and ethical considerations, making widespread adoption difficult.
Let’s go through some of the major challenges and limitations:
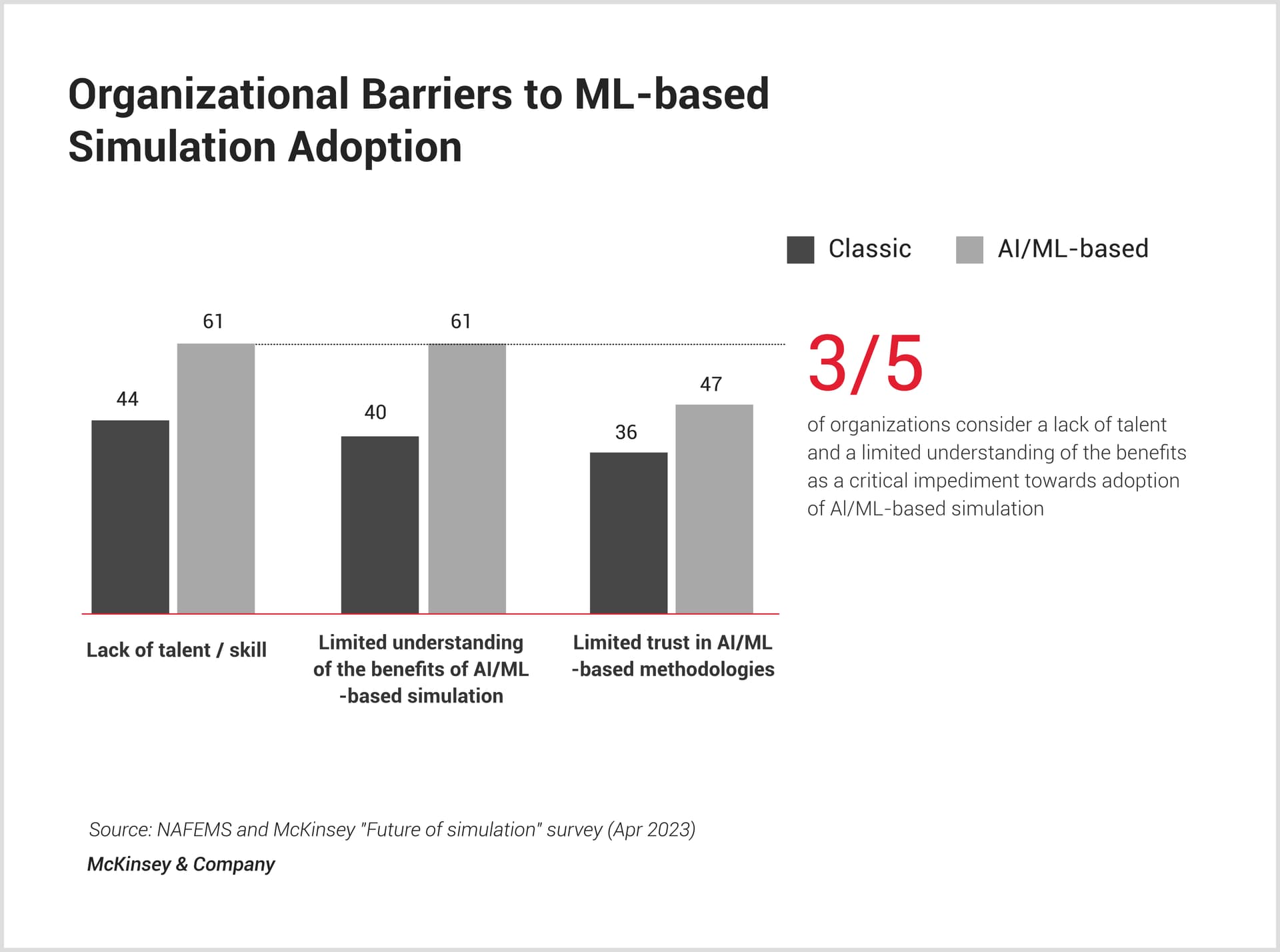
Organizational Barriers
A shortage of skilled talent (61%), limited understanding of ML benefits (61%), and trust issues in AI/ML (47%) hinder adoption. Addressing this requires upskilling, awareness programs, and validation to build trust and drive change.
Data Dependency and Quality
High-quality, labeled datasets are essential for ML algorithms and simulations, but acquiring and curating these datasets is resource intensive. Poor data quality can lead to unreliable models and affect the accuracy of AR/VR/MR simulations, complicating their integration and management.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Industries relying on legacy systems face compatibility issues when trying to integrate advanced AR/VR/MR simulations and ML technologies. Significant upgrades or replacements of existing infrastructure may be required, slowing down adoption and increasing costs.
Cost and Complexity
Developing accurate simulations and ML models requires substantial computational resources and specialized expertise, making them costly and complex to implement.
Ethical Considerations: ML and simulation models can inadvertently inherit biases in training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes (Deloitte). Simplified simulations may overlook real-world complexities, leading to flawed strategies or decisions, especially in safety-critical scenarios.
The Future of ML and Simulation Technologies
ML and simulation technologies are revolutionizing manufacturing by driving efficiency, innovation, and sustainability. Emerging trends, such as the integration of ML with IoT and digital twins, enable dynamic, predictive systems like self-learning supply chains.
This convergence empowers businesses, including SMEs, to adopt Industry 4.0 solutions, leveling the playing field. Simulation-driven innovations are also tackling global challenges, from urban planning to climate change, creating smarter, more sustainable cities.
As these technologies evolve, they are set to transform industrial operations, making it essential for enterprises to invest in them to remain competitive in the digital revolution.
Visit our websitefor more information on AI-powered solutions.
