From Legacy to AI: The Evolution of Data Protection and Compliance
31 October, 2024
As the digital frontier expands, so does the battleground for data protection. The cost of data breaches continues to soar, reaching a record high of $4.88 million on average in 2024, marking a 10% increase from the previous year (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024). Additionally, one in three breaches now involves 'shadow data'—overlooked and unprotected information. With AI playing a pivotal role in security, it offers substantial savings, however, the rapid evolution of AI underscores the pressing need for immediate and robust regulatory reforms.
Even more alarming, one in three breaches now involve “shadow data"—sensitive data that is often overlooked and unprotected. Enterprises using AI for security can save an average of $2.22 million, but this emerging technology demands swift regulatory action (Cost of a Data Breach Report 2024).

As AI reshapes industries, immediate, adaptive data protection laws are essential to ensure privacy keeps pace with innovation.
The Evolution of Data Protection with the Rise of the Internet
In the early days, data protection was a simpler task. Most of it involved keeping physical records secure and managing basic digital systems with a focus on confidentiality, integrity, and availability—what we now call the CIA triad.
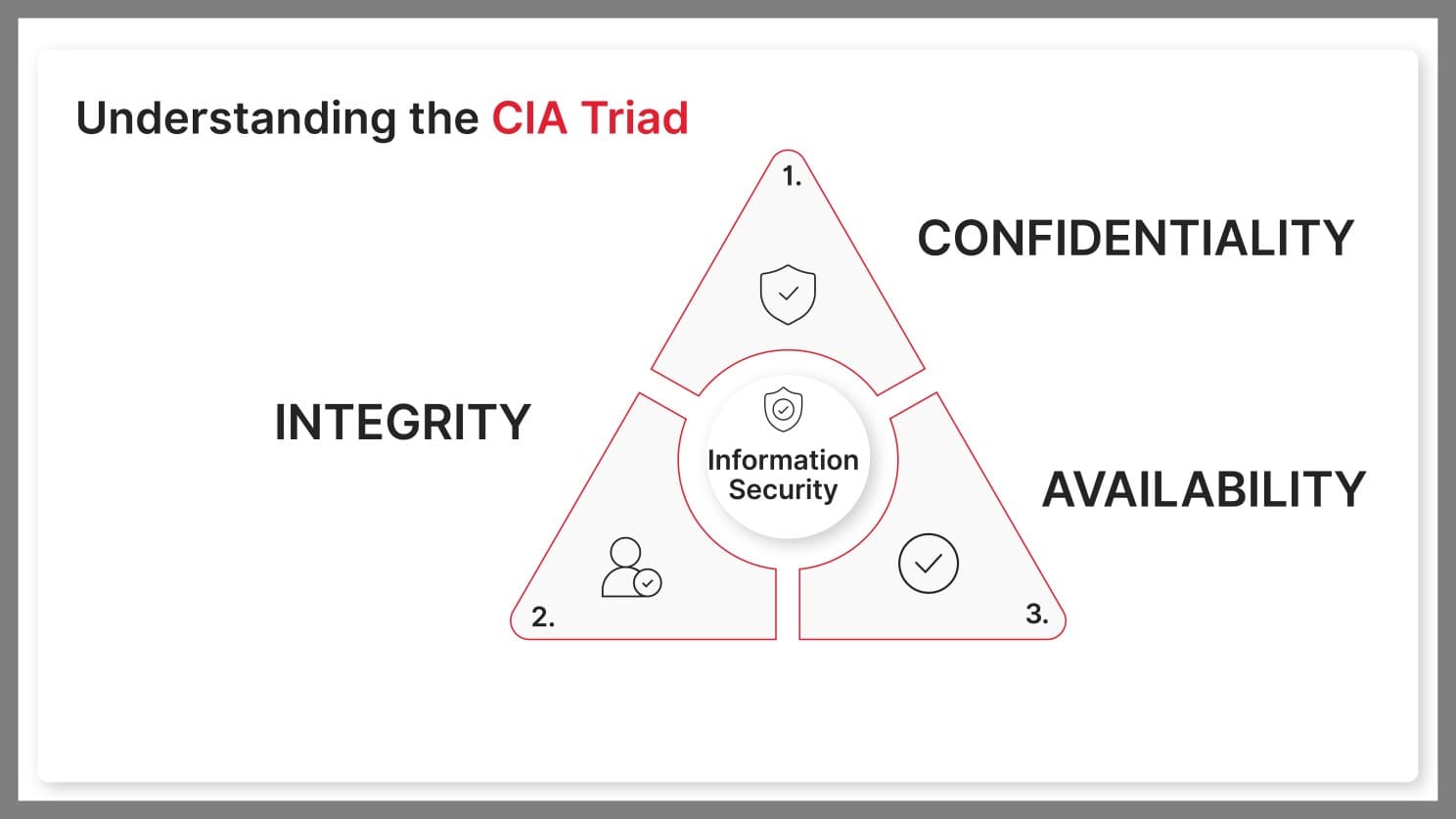
But with the internet and connected devices came a whole new world of data collection, where massive amounts of personal and sensitive information could be stored and accessed across digital networks.
Suddenly, data wasn’t just an asset; it became a major liability too. As businesses went digital, they faced new risks of breaches and cyberattacks, highlighting the urgent need for stronger data protection measures. This shift laid the groundwork for the modern data privacy laws we have today.
Tech Giants and the Slow Rise of Compliance
During their early growth phases, Tech giants such as Google and META amassed vast amounts of personal data with minimal oversight, leveraging user data to grow into powerful entities. However, as their influence grew, so did public concern over privacy and data misuse.
This tension is highlighted in the timeline of GDPR's evolution, which showcases key milestones that shaped the EU's robust data protection framework.
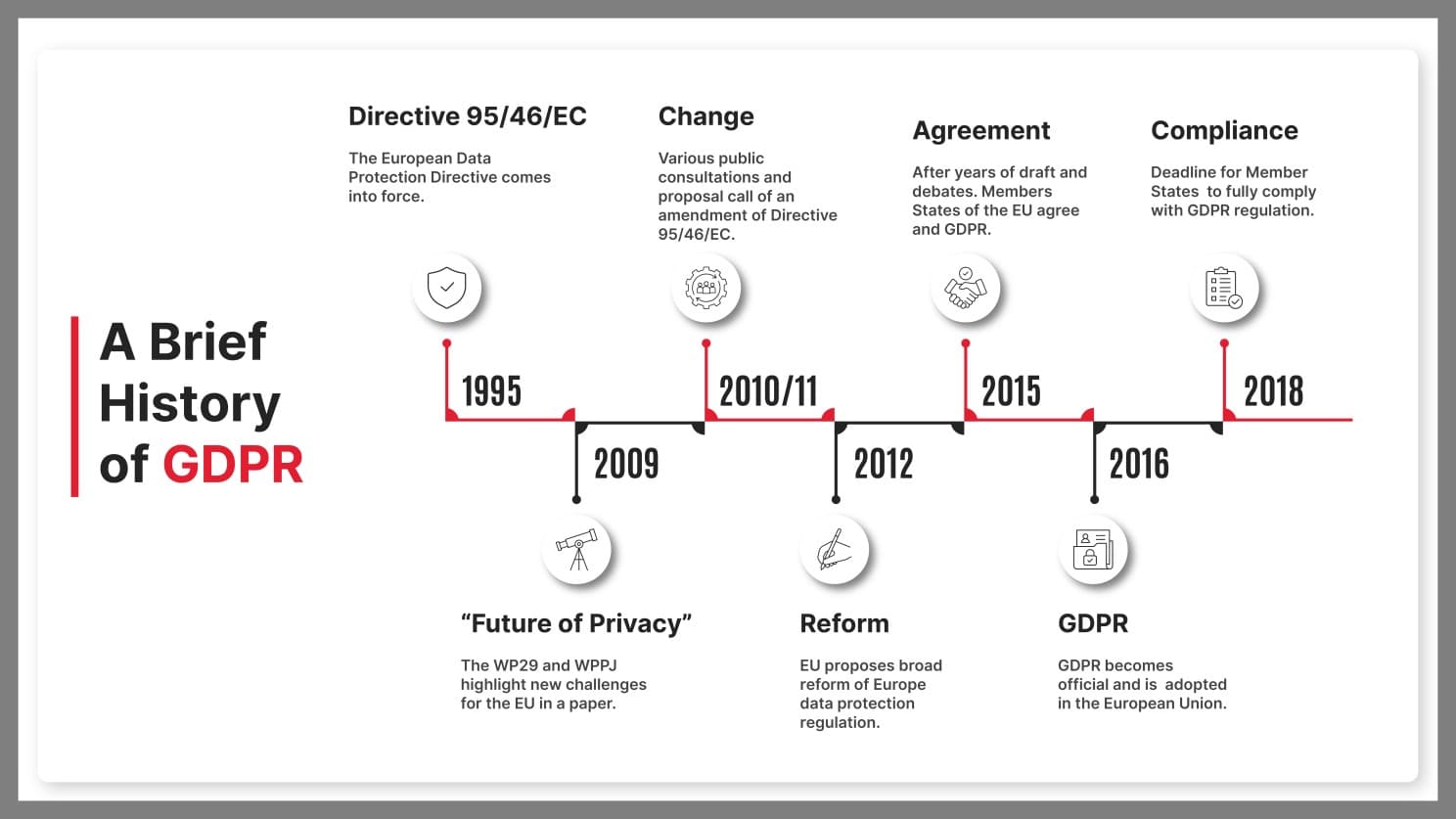
Regulatory responses were initially slow, but the tide began to shift with landmark data protection laws like the GDPR in the European Union and the CCPA in California. Implemented in 2018, the GDPR introduced strict requirements on consent and data usage, setting a global standard. Similarly, the CCPA, effective in 2020, empowered Californian consumers with rights over their personal information.
These regulations compelled the Tech giants to adopt more transparent and accountable data practices, ultimately reshaping the landscape of digital privacy and setting a precedent for new laws to come.
The Ripple Effects of Data Laws on Consumer Privacy
As data protection laws evolve, their influence extends far beyond the corporate world, permeating the everyday lives of consumers. This section delves into how these regulations are reshaping consumer privacy and the broader societal implications.
Impact on Consumers:
Data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA have significantly influenced consumer awareness and control over personal data. Consumers are increasingly aware of how businesses handle their data, with regulations providing them more rights to access, control, and even request the deletion of their data. For instance, since the enactment of GDPR, about 60% of European consumers have become aware of the regulations governing their data, compared to 40% in 2015 (McKinsey & Company).
However, despite these rights, there is still a substantial gap in consumer understanding and actual control over personal data, as evidenced by findings that a large percentage of Europeans feel they have little control over their personal information (Center for Data Innovation).
Consumer Reactions:
Consumers are responding by becoming more selective with whom they share their data, often opting out of services that do not align with their privacy expectations. A McKinsey report noted that consumers might stop engaging with companies that have poor data-privacy practices (McKinsey & Company). This growing consumer sensitivity to data privacy is paralleled by an increase in consumer expectations for businesses to handle data responsibly.
Behavioral Trends:
Despite heightened concerns, consumer behavior toward digital adoption continues to be robust. For example, the adoption of subscription video-on-demand services has seen significant growth, even among consumers expressing concerns about data privacy (Deloitte United States). This indicates a complex relationship between privacy concerns and digital service usage, suggesting that while consumers are concerned, they continue to value the benefits provided by digital services.
New Technologies, New Challenges – Why Every Innovation Needs Immediate Regulation
Each wave of technology has introduced privacy risks that quickly outpaced regulatory frameworks, often catching regulators off guard. The internet enabled extensive data collection with limited user control, raising concerns over personal data tracking, while social media introduced new vulnerabilities, like unauthorized third-party access, exemplified by the Cambridge Analytica scandal.
Delayed regulation around the renowned tech giants allowed companies to gather and misuse personal data with little accountability. Incidents like Cambridge Analytica where 50 million Facebook profiles were harvested in a in major data breach revealed how sensitive information could be manipulated for influence, pushing lawmakers to establish stricter frameworks, like GDPR and CCPA (Cambridge Analytica).
These high-profile cases underscore the consequences of regulatory lag, with public outcry often serving as the final push for action. If AI, with its advanced data processing capabilities, follows a similar path, it could expose users to unprecedented privacy risks.
To avoid repeating past mistakes, proactive, adaptive regulation is essential as AI reshapes the digital landscape.
AI and Data Privacy – A New Frontier in Compliance
AI inherently gathers and processes vast amounts of data to continuously improve and adapt, making it both powerful and potentially risky. Unlike traditional systems, AI’s rapid self-learning and adaptation exposes it to unique privacy vulnerabilities, including data misuse and bias.
Early examples, like AI-driven facial recognition leading to racial bias or discriminatory algorithms in hiring, highlight the dangers when AI systems unintentionally exploit sensitive data. AI misuse has already enabled sophisticated attacks, such as the $25 million fraud involving deepfake technology (Fortune).
Delaying regulations for AI could open the door to larger privacy and ethical violations, underscoring the need for proactive, adaptive laws.
Role of AI in Modern Data Protection and Compliance
AI is reshaping compliance by automating monitoring, breach detection, and quickly flagging anomalies, reducing breach containment time by 108 days (IBM). Unlike Google and META, which struggled with slow adaptation to regulations, AI’s adaptability enables proactive, real-time compliance, minimizing data vulnerability during regulatory delays.
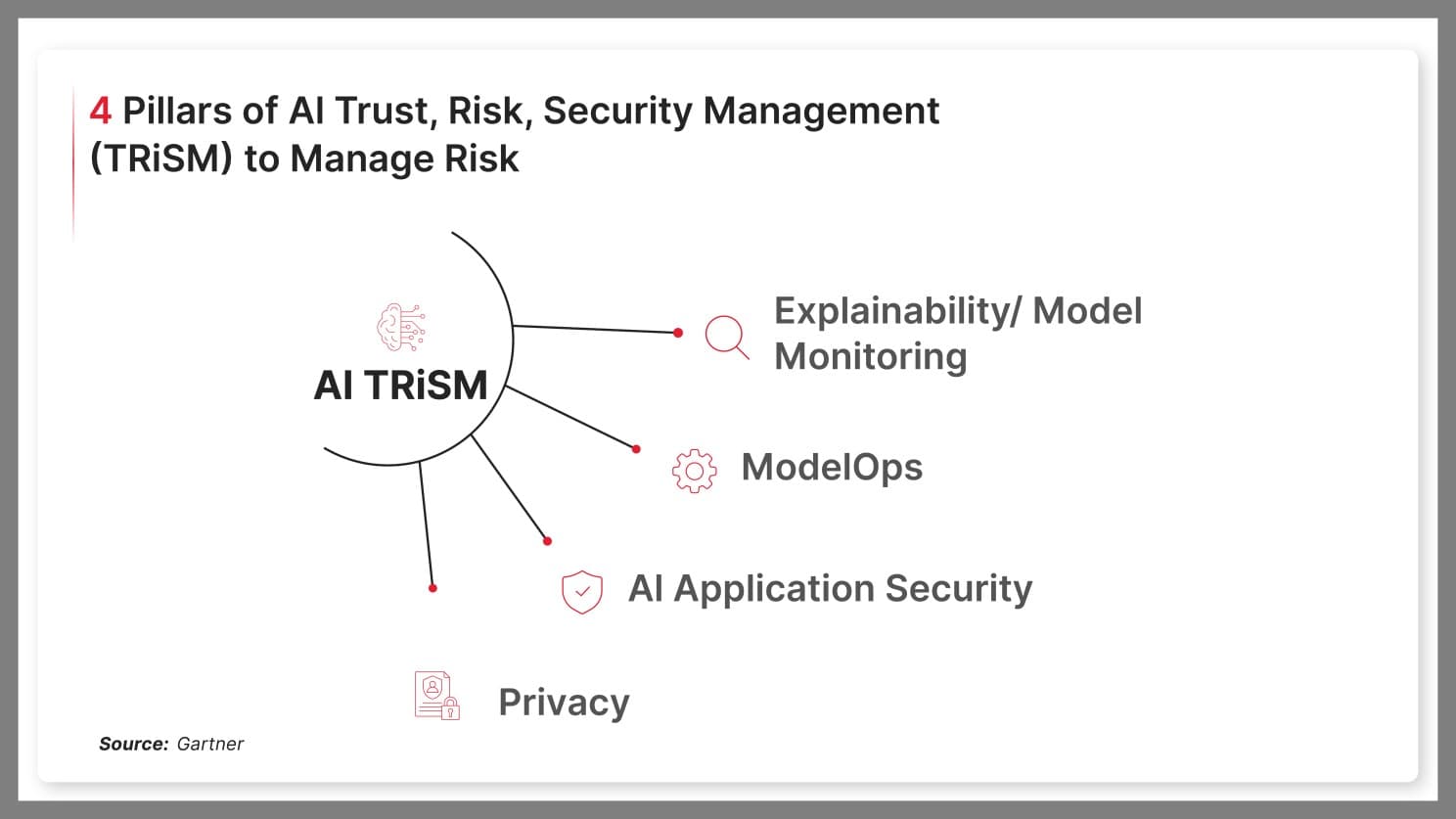
Building on AI’s adaptability in compliance, Gartner’s AI TRiSM framework enhances this proactive approach by ensuring AI models are secure, transparent, and privacy-focused. TRiSM’s four pillars cover essential areas:
- Explainability and Model Monitoring: Ensures transparent decisions and detects anomalies
- ModelOps: Manages AI lifecycles for consistent, compliant operations
- AI Application Security: Protects against adversarial attacks with targeted security measures
- Privacy: Maintains data privacy by verifying data use and limiting sensitive information
With frameworks like TRiSM driving proactive compliance, regulatory bodies worldwide are stepping up to establish robust guidelines for AI governance.
Regulatory Bodies and Their Actions on AI Compliance
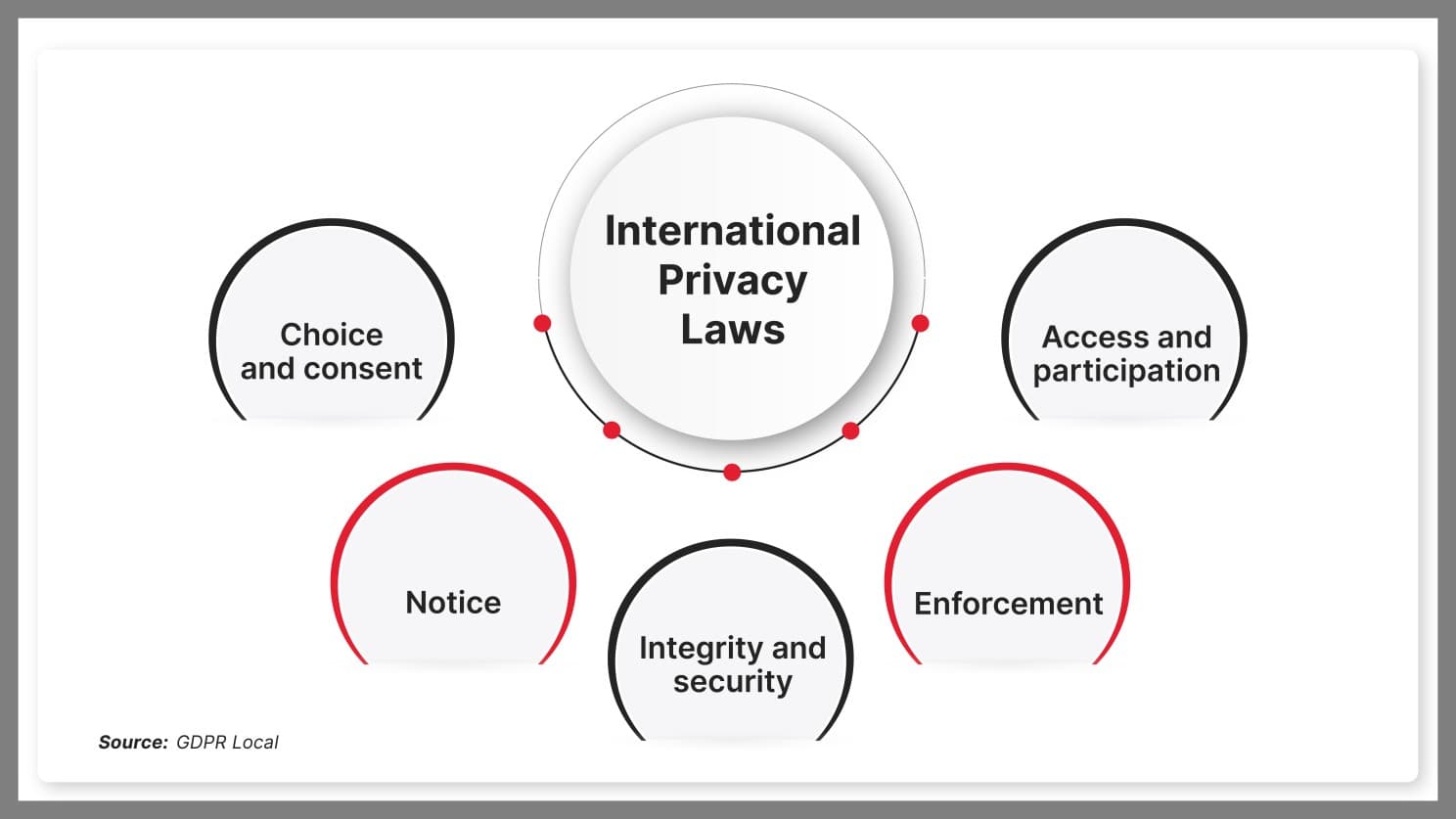
International privacy laws are anchored by core principles, Choice and Consent, Access and Participation, Integrity and Security, Notice, and Enforcement—ensuring robust data rights and protections across diverse regulatory landscapes.
The European Union has strengthened global AI compliance through its GDPR foundation by implementing the AI Act, which sets strict guidelines for managing AI risks. This Act categorizes applications into tiers—unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal risk—reinforcing its commitment to data protection in the AI era
This Act, effective in August 2024, mandates high standards, especially for high-risk applications like biometric surveillance, with fines of up to €40 million or 7% of global turnover. Similar to GDPR, the AI Act applies to any AI system operating within the EU, setting a precedent inspiring regulatory efforts globally, including in the UK, Brazil, and Canada.
In the U.S., states like California advance AI regulation through CCPA expansions, giving consumers more control over data used by AI systems. Together, these regulatory frameworks aim to balance innovation with robust protections against AI’s unique risks, like data misuse, privacy invasion, and lack of transparency, creating a unified approach to AI governance.

The Future of AI Compliance and Data Protection
Over the next decade, AI compliance will evolve to tackle privacy and security challenges from technologies like generative AI, LLMs, and particularly agentic AI. As AI systems gain autonomy, ensuring that they operate within ethical and legal boundaries becomes crucial. Regulations will emphasize transparency, traceability, and accountability, with strict standards designed to prevent privacy breaches and manage the complex decision-making processes of agentic AI.
As AI integrates into sectors like healthcare, finance, and consumer services, regulatory bodies will require alignment with frameworks like GDPR. This means not only maintaining oversight but also adapting these frameworks to address the challenges posed by AI systems that can act independently. For enterprises, this involves investing in data-centric security, embedding privacy by design, and adopting clear governance policies to ensure data remains secure and compliant amidst rapid technological advancement.
Conclusion
The rapid rise of AI has exposed critical gaps in regulatory frameworks, underscoring a longstanding pattern of delayed response to emerging technologies. Unregulated, AI poses significant privacy and security risks, but it also presents an opportunity: by establishing fast-adapting data protection laws, we can secure AI’s benefits while safeguarding personal information.
Learning from past tech revolutions, the focus should be on proactive, transparent compliance standards. As a globally trusted, AI-first digital transformation company, CodeNinja helps enterprises navigate these complexities, ensuring robust, responsible AI solutions across diverse industries to build trust with customers and provide memorable customer experiences.
Visit our website for more details.
